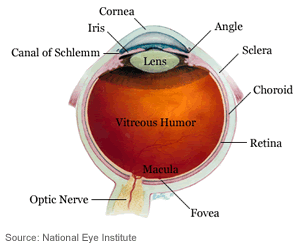
Cornea
The cornea is a clear, dome shaped covering and it serves as the eye’s main lens.
Fovea
The fovea is located in the center of the macula, it is where vision is the most acute.
Iris
The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye. The color of the eye depends on the color of the iris.
Lens
The lens is secondary to the cornea and is used for fine tuning the focus.
Macula
The macula is a small, sensitive area of the central retina used for fine visual skills such as reading.
Optic Nerve
The optic nerve carries the signals from the retina to your brain. The brain translates this visual information into images that you see.
Retina
The eye focuses light on the retina. The retina is where light receptor cells translate light into signals that go to the brain.
Cones and rods are specialized light-sensitive cells (photoreceptors) in the retina. Cones provide sharp central vision and color vision. Rods handle side vision and vision in dim lighting conditions.
Sclera
The sclera is the thick, white outer layer of the eyeball and it serves as protection along with the cornea.
Courtesy of the National Eye Institute